Storage Spaces Direct (S2D) is the award-winning software-defined storage (SDS) tecnhology that was first introduced in Windows Server 2016. Since that moment, S2D has become my one of the favourite and frequently used role in Windows Server (on-premises and even in Azure).
Windows Server 2019 that is going to be generally available in the second half of this year (September or October – in accordance with WS 2012-2016 release dates) continues to develop S2D by adding new features. Why don’t we discuss them right now?
TIP: Windows Server 2019 preview build is available here
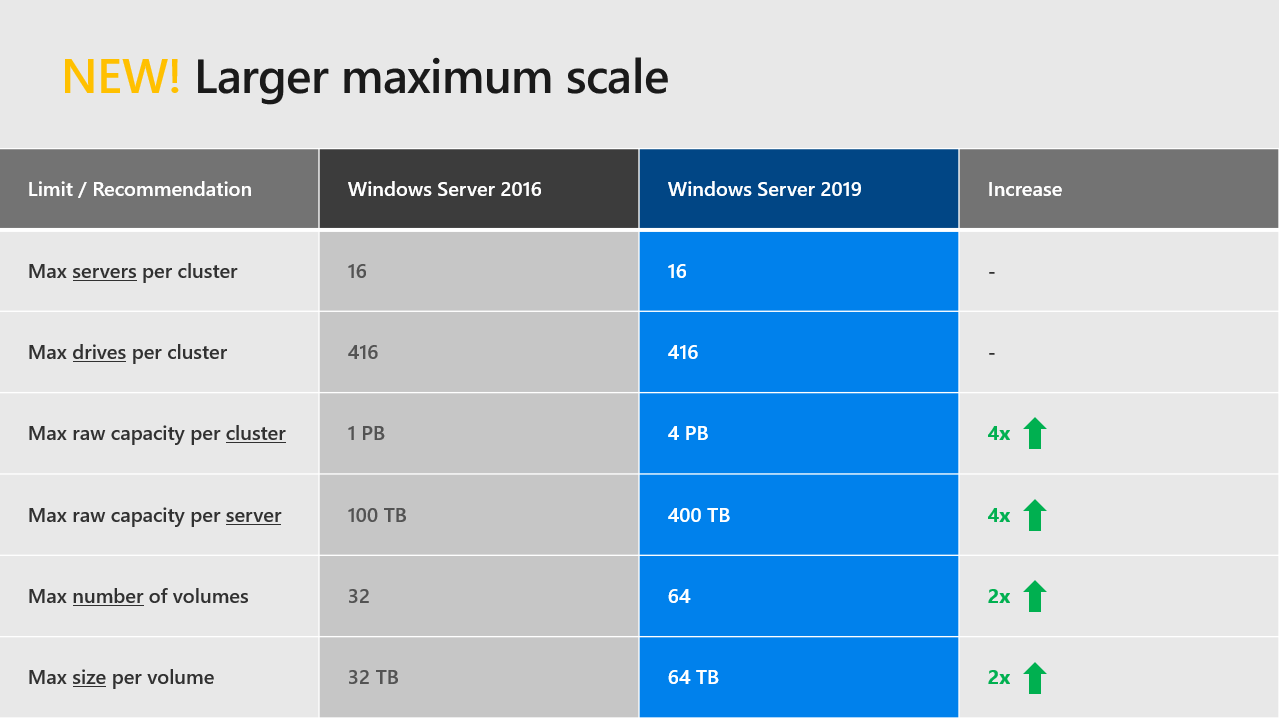
Scalability
More volumes, bigger capacity per server and cluster
USB Witness
Storage Spaces Direct can be configured with just two nodes. However, we will need to design witness placement to protect our cluster from unexpected failure (in other words, we should achieve quorum). In Windows Server 2016, you can place witness on a file share, cloud (details here) or disk witness (it’d be very strange if it was actually used in S2D clusters). What about customers who don’t have any AD infrastructure or Azure/Internet access? Here is a breakthrough – USB Witness.

In short, you will be able to configure a true two-node S2D by using USB thumb drive connected to the router that is already used for VM/management traffic between nodes, for instance. Other two network interfaces (shown on the picture above), could be RDMA-adapters (recommended and supported) or Thunderbolt (POC, Project Kepler-47).
Simply insert the USB drive into the port on the router, set the share name and access information, configure witness in PowerShell: Set-ClusterQuorum -FileShareWitness \path\ -Credential and you are ready to go.
TIP: the router should support SMB2+ and USB. And, given that a witness.log is a quite small file (just kilobytes), you can use any-sized USB drives. The list of the supported routers will be available later.
Data Deduplication
ReFS is the recommended file system for S2D, improves VHDX creation/expansion speed (enables Accelerated VHDX operations), provides higher stability by detecting corruptions and allowing you to repair them with no volume downtime. However, some features such as ODX, Data Deduplication are not supported by ReFS in Windows Server 2016.
Starting with the Windows Server 2019 (1709 and later), Data Deduplication has been fully supported for ReFS. It means that you no longer need to choose between NTFS and ReFS file systems while planning S2D volumes. Create ReFS volume, enable Data Deduplication (PowerShell/Windows Admin Center), and then check the savings of storage space (use PowerShell and Get-DedupVolume cmdlet).

Proactive outlier detection
It was quite challenging to investigate performance issues in S2D in Windows Server 2016. We had to use PowerShell or performance counters (+VMFleet) to get a full picture of our setup’s behavior. Windows Server 2019 significantly simplifies that. S2D now records the outcome (success/failure) and latency (elapsed time) for every read/write IO to every drive without any performance impact. Therefore, drives with latency/outcome issues will be marked in PowerShell and Windows Admin Center as “Abnormal Latency” status. In addition, you can organize pooled drives into peer groups, and then compare latency against peers to quickly find any bottlenecks (new cmdlet: Get-PhysicalDiskIoReport).
This azure-inspired mechanism works on the lower level than performance counters and enabled by default for every SATA,SAS,NVMe drives.

Others
-Faster mirror-accelerated parity volumes (~x2)
-PMEM (Persistent Memory) drives support (Intel Optane/NVDIMM-N) for use as cache and capacity
-Deep integration with Windows Admin Center (a free HTML5-based management interface for entire Windows Server infrastructure. We’ll look at this a bit later)
-New networking recommendations for high performance, at scale, or deployments of 4+ nodes: 25 Gbps (or higher) NICs (two or more) that are remote-direct memory access (RDMA) capable, iWARP (recommended) or RoCE




